Java Concurrent(二)::并发集合
上一篇文章简单介绍了一些多线程互斥/同步操作的知识,这篇将介绍一些java.util.concurrent包下的常用并发集合。
BlockingQueue
阻塞队列是生产者——消费者模式中常用的数据结构,上一篇中我们用两个Condition实现了一个有界阻塞队列,其实Java Concurrent包中已经有阻塞队列的一些列实现,让我们先来看看Java中BlockingQueue接口:
//接口继承自Queue接口
//同样提供非阻塞的队列接口
public interface BlockingQueue extends Queue {
//我们着重看下阻塞方法
//阻塞写入队列,如果队列已满,阻塞等待
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this queue, waiting if necessary
* for space to become available.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
void put(E e) throws InterruptedException;
//带超时时间的阻塞写入队列
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this queue, waiting up to the
* specified wait time if necessary for space to become available.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @param timeout how long to wait before giving up, in units of
* {@code unit}
* @param unit a {@code TimeUnit} determining how to interpret the
* {@code timeout} parameter
* @return {@code true} if successful, or {@code false} if
* the specified waiting time elapses before space is available
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this queue
*/
boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
//阻塞读方法,如果队列为空,阻塞等待
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting if necessary
* until an element becomes available.
*
* @return the head of this queue
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
*/
E take() throws InterruptedException;
//带超时时间的阻塞读方法
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting up to the
* specified wait time if necessary for an element to become available.
*
* @param timeout how long to wait before giving up, in units of
* {@code unit}
* @param unit a {@code TimeUnit} determining how to interpret the
* {@code timeout} parameter
* @return the head of this queue, or {@code null} if the
* specified waiting time elapses before an element is available
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
*/
E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
}
ArrayBlockingQueue & LinkedBlockingQueue
BlockingQueue最简单的两个实现就是ArrayBlockingQueue和LinkedBlockingQueue,通过名字就可以看出来,分别是用数组和链表实现的。
- ArrayBlockingQueue内部使用Object []item数组存放元素,put/take的时候使用lockInterruptibly加锁,并且用fullCondition EmptyCondition进行await/signal
//容量为3的阻塞队列,非公平锁
BlockingQueue queue1 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
//容量为3的公平锁阻塞队列
BlockingQueue queue2 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3, true);
//带初始值的容量为3的非公平锁阻塞队列
Collection collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
collection.add(3);
//collection.add(4); 如果超过容量(3),那么抛出IllegalArgumentException
BlockingQueue queue3 = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3, false, collection);
- LinkedBlockingQueue
LinkedBlockingQueue内部使用链表存储元素,使用两个ReentrantLock类型的锁分别作为takeLock和putLock
//默认容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE的阻塞队列
BlockingQueue queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
//容量为3的阻塞队列,非公平锁
BlockingQueue queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(3);
//容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE的阻塞队列,初始值
Collection collection = new ArrayList<>();
collection.add(1);
collection.add(2);
collection.add(3);
BlockingQueue queue1 = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(collection);
//LinkedBlockingQueue只能使用非公平锁
PriorityBlockingQueue
PriorityBlockingQueue是带优先级的阻塞队列无上限,常用于优先级任务调度! 内部用数组组成一个大顶堆来维护元素; 使用一把ReentrantLock锁控制线程安全; 优先级队列由于没有上限,所以put方法不会被阻塞; take在队列空的条件下阻塞; 此外由于无上限队列,PriorityBlockingQueue内部用CAS乐观所进行扩容操作,扩容的方法tryGrow:
/**
* Tries to grow array to accommodate at least one more element
* (but normally expand by about 50%), giving up (allowing retry)
* on contention (which we expect to be rare). Call only while
* holding lock.
*
* @param array the heap array
* @param oldCap the length of the array
*/
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {
lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lock
Object[] newArray = null;
//allocationSpinLock作为乐观锁,进行CAS操作
//只有获得乐观锁的线程才会实例化newArray
if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,
0, 1)) {
try {
int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?
(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small
(oldCap >> 1));
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflow
int minCap = oldCap + 1;
if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)
newArray = new Object[newCap];
} finally {
allocationSpinLock = 0;
}
}
//没有获得锁的线程newArray == null
if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocating
Thread.yield();
lock.lock();
if (newArray != null && queue == array) {
queue = newArray;
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);
}
}
BlockingQueue queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
//构造函数还可以传入initialCapacity和Comparator类
queue.put(2);
queue.put(3);
queue.put(0);
for(Integer i:queue){
System.out.println(i);
}
//Iterator没有按顺序
//0 3 2
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(queue.take());
}
//take会按大小顺序
//0 2 3
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
LinkedList集合是非线程安全的,在多线程并发环境下进行修改的话,可能遇到java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常; 在concurrent包中为我们提供了一个ConcurrentLinkedQueue类,在一些场景下可以替代LinkedList。
不像LinkedBlockingQueue,ConcurrentLinkedQueue只是Queue接口的实现类,并没有阻塞读写接口;
同样的对于非阻塞的offer/poll方法,它们都是线程安全的,但是LinkedBlockingQueue内部使用ReentrantLock锁保证线程安全,ConcurrentLinkedQueue则使用CAS乐观锁;
类图:
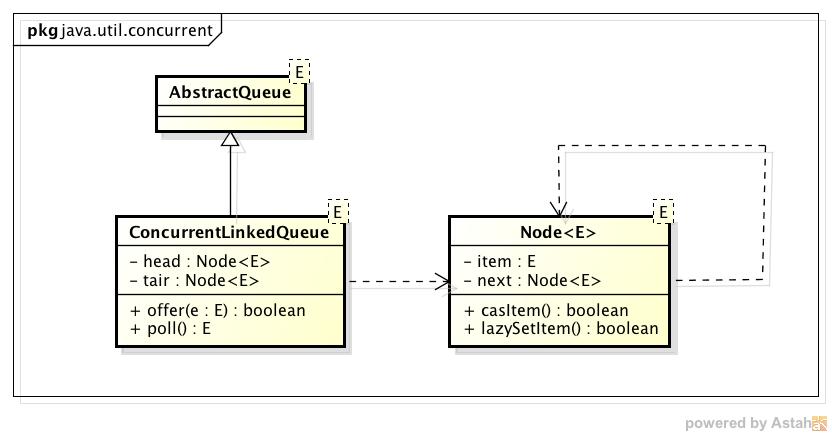
ConcurrentLinkedQueue实现类中有两个变量head和tail分别指向队头和队尾,offer/poll操作需要用到tail/head,并更新它们的值。
但是注意tail不一定指向最后一个元素,也可能是tail.next指向最后一个元素,同样head不一定是第一个元素,第一个元素也可能是head.next
这样做尽可能的减少offer/poll时CAS冲突概率。
ConcurrentLinkedQueue初始状态
head=tail=new Node<>(null);
offer源码如下
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final Node newNode = new Node(e);
for (Node t = tail, p = t;;) {
Node q = p.next;
if (q == null) {
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
if (p != t)
casTail(t, newNode);
return true;
}
//CAS失败,说明已经有其他线程offer或者poll了
}
else if (p == q)
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
单线程offer:
第一个元素(第奇数个元素)入队列
- 进入line6分支
- 新元素插入tail.next
- 此时p==t,不更新tail
第二个元素(偶数个元素)入队列
- q=tail.next为第一个元素,p=tail
- 进入line16分支
- p==t==tail,所以更新p=q
- 循环line5,此时q为null,进入line6
- 插入新节点,并且p!=t,更新tail为新节点
多线程offer:
多线程冲突(其他线程先于当前线程修改过)情况下
- 上面line7的CAS操作会失败(已经有其他线程在tail.next插入新元素,但是还没有更新tail)
- line16分支,p指向q(也就是tail.next)节点(此时tail.next节点已经不是null,被其他线程插入新元素)
- line5更新q为p.next,此时为null
- 重新竞争CAS乐观锁,如果成功,则在末尾插入新元素,同时更新tail
poll源码如下
public E poll() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
for (Node h = head, p = h, q;;) {
E item = p.item;
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {
if (p != h)
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
return item;
}
else if ((q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
else if (p == q)
continue restartFromHead;
else
p = q;
}
}
}
单线程poll:
元素在head.item
- p.item==null,进入line6,同时CAS锁成功,更新head.item值为null
- p==h,不需要更新head
- 返回item
元素在head.next.item
- head.item此时为null,
- 如果head.next==null,说明队列空,进入line11,返回null
- 否则判断p==q(单线程下一定不想等)
- 最后进入line17, p指向下一个节点,也就是head.next
- 循环line5,此时p.item!=null(head.next.item!=null),修改item=null
- line7处p已经为head.next, h为head,故更新head
多线程poll:
多线程冲突(其他线程先于当前线程修改过)情况下
- line6 CAS操作item时冲突
- 进入line15,重新从head开始出队列
相较于LinkedBlockingQueue,ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用乐观锁控制线程安全,因此适用于写比较少,冲突不是特别多的场景下。
CopyOnWriteArrayList & CopyOnWriteArraySet
Copy-On-Write简称COW,是一种用于程序设计中的优化策略。其基本思路是,从一开始大家都在共享同一个内容,当某个人想要修改这个内容的时候,才会真正把内容Copy出去形成一个新的内容然后再改,这是一种延时懒惰策略。从JDK1.5开始Java并发包里提供了两个使用CopyOnWrite机制实现的并发容器,它们是CopyOnWriteArrayList和CopyOnWriteArraySet。CopyOnWrite容器非常有用,可以在非常多的并发场景中使用到。
只有在修改add/remove操作时,才需要加锁,可以做到并发free-lock读,适用于读多写少的场景,并且数据量不宜过大,否则copy锁组时间过长。
ConcurrentMap
ConcurrentMap继承自Map接口,同时主要提供了putIfAbsent方法:
public interface ConcurrentMap extends Map {
V putIfAbsent(K key, V value);
}
putIfAbsent方法与put方法的区别就是:
putIfAbsent(k, v)如果k存在,v不覆盖map中的值
put(k, v) 如果k存在,则v覆盖map中的值
If the specified key is not already associated with a value, associate it with the given value. This is equivalent to
{ if (!map.containsKey(key)) return map.put(key, value); else return map.get(key); }except that the action is performed atomically.
ConcurrentHashMap
ConcurrentMap最常用的实现类就是ConcurrentHashMap了,对于同样是线程安全的Hashtable,不同点是:
- Hashtable是接口Map的实现类,没有putIfAbsend方法;
- Hashtable使用synchronized关键字,锁住整个Map,锁的力度比较大。
下面让我们来看看ConcurrentHashMap是如何保证线程安全的
- get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0) //表示是一个被回收的solt
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}
- put/putIfAbsent方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, true);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node[] tab = table;;) {
Node f; int n, i, fh;
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
else {
V oldVal = null;
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
上面代码line14 casTabAt采用乐观锁添加新Node,冲突则循环重试
line22 只锁住单个Node,减少锁的粒度,提高并发性能
总结:
通过看JDK Concurrent集合源码,发现考虑多线程的情况下,一个简单的集合操作逻辑也会变的非常复杂,因此自己在项目中一定要好好设计,争取做到:
- 能用单线程就别用多线程;
- 多用JDK里封装好的并发工具,自己代码逻辑尽量在单线程中;
- 使用final不变量,没有变量,线程之间就可以不考虑锁;
- 尽量多使用局部变量;由于局部变量存在栈上,每个线程独享自己的栈空间,而堆上的对象则是jvm共享;
- 状态变化尽量保持在一个线程中,多个线程都能改变共享变量的状态会比较麻烦;
- 锁的粒度尽可能小;
参考资料:
相关文章: